How To Run a Troubleshooter For PC Issues on Windows [Windows 11/10]
Dealing with computer issues can be a real hassle. Slow performance, system crashes, and unexpected error messages often get in the way. Fortunately, Windows includes built-in tools designed to diagnose and resolve these problems efficiently.
Learning to run a troubleshooter for PC issues on Windows can save you time and money. You don’t need to call tech support for every small problem.
Windows troubleshooters can fix many common issues automatically.
Part 1: What is a Windows Troubleshooter?
A Windows troubleshooter is a built-in utility. It is designed to identify and resolve common PC issues. It runs a system scan to detect problems—like network failures, audio glitches, or update errors—and then attempts to fix them automatically. You can think of it as your computer’s built-in technician. A technician who runs quietly in the background to keep things running smoothly.
These tools come pre-installed with Windows 11 and Windows 10. Microsoft created them to help users. They solve common PC problems. They run tests on your system. Each part is checked for issues. When problems are found, they apply known fixes. The process is automatic. You don’t need to do much. It’s quick and simple. Just follow the steps and let it work.
Part 2: Why Use a Windows Troubleshooter? How Does It Help?
Windows troubleshooters offer many benefits for PC users. They provide quick solutions without technical knowledge. Here are the main reasons to use them:
- Saves time – Fixes issues in minutes. No need to spend hours searching online or adjusting settings manually. It handles the technical work so you don’t have to.
- Free solution – No payment required. Avoid expensive tech support or repair shops. You get reliable fixes without spending a single rupee.
- Easy to use – Simple layout and clear steps. No technical knowledge needed. Just follow the prompts and let it do the rest.
- Automatic detection – Scans your system for hidden problems. Finds issues you might miss, like background errors or misconfigured settings.
- Safe repairs – Uses trusted Microsoft fixes. No risk to your files or system. Every solution is tested and secure.
- Multiple problem types – Handles network, audio, display, and performance issues. From slow Wi-Fi to sound failures, it covers the most common problems.
- Step-by-step guidance – Shows what it’s checking and fixing. You stay informed at every stage. No guesswork or confusion.
- Detailed reports – Explains what went wrong and how it was fixed. Gives you a clear summary with recommendations to avoid future issues.
Part 3: Advantages/Disadvantages of Using Windows Troubleshooter
Every tool has pros and cons. Understanding both sides helps you use troubleshooters effectively.
Advantages:
- Quick problem detection and resolution – Finds and fixes issues fast. No long waits or complicated steps.
- No technical skills required – No tech skills needed. Just follow the on-screen instructions.
- Completely free to use – No cost at any stage. No subscriptions, fees, or hidden charges.
- Safe and reliable fixes – Uses trusted solutions. Keeps your system stable and secure.
- Works offline without internet – Runs without a connection. Perfect for fixing problems when you’re offline.
- Covers most common PC issues – Handles network, audio, display, and performance problems. Solves everyday tech headaches.
- Provides clear explanations – Tells you what went wrong and how it was fixed. No jargon, just plain language.
Disadvantages:
- Cannot fix complex hardware problems – Doesn’t handle issues with physical components like faulty motherboards or damaged ports.
- Limited to known Microsoft solutions – Only applies fixes that are officially supported. It won’t offer custom or third-party solutions.
- May not work for newer issues – Might not recognize problems introduced by recent updates or new hardware.
- Sometimes gives generic advice – In some cases, suggestions may be broad or not tailored to your exact setup.
- Cannot repair physical damage – Won’t help with broken screens, cracked cases, or other physical defects.
- May miss rare or unique problems – Uncommon errors or system-specific bugs might go undetected.
Part 4: Precautions to Take When Using Windows Troubleshooter for Fixing Issues
Taking precautions protects your data and system. Always prepare before running any diagnostic tools. Follow these safety steps:
- Create a backup – Save your important files before making any system changes. It’s a simple step that keeps your data safe if something unexpected happens. Backing up ensures you won’t lose documents, photos, or settings during repairs or updates.
- Close running programs – Stop other apps to avoid conflicts during troubleshooting. It helps the tool work more efficiently.
- Check system updates – Install the latest Windows updates first. Some issues may already be fixed by newer patches.
- Note current settings – Write down your current configurations. You may need to restore them later if changes don’t work.
- Run as administrator – Use admin rights for full access. This ensures the troubleshooter can make necessary system changes.
- Avoid interrupting – Let the troubleshooter complete its full scan. Interrupting may prevent it from finding or fixing problems.
- Review suggested changes – Read what the tool wants to change before accepting. Make sure you understand what will be modified.
- Test after fixes – Verify that problems are actually solved before finishing. Try using the affected features to confirm everything works.
Part 5: How to Run a Troubleshooter for PC Issues on Windows 11/10?
Running troubleshooters is simple once you know where to find them. Windows provides several ways to access these helpful tools.
For Windows 11:
Method 1: Through Settings
The Settings app is the modern way to access troubleshooters. It works best for Windows 11 users. The interface is clean and simple. Menus are easy to navigate. You don’t need technical skills. Just follow the steps and run the tool. It’s quick and beginner-friendly.
This approach gives you access to all available troubleshooters in one place. The Settings app organizes tools by category. You can see which troubleshooters are available for your specific problems.
- Click the Start button. Select “Settings” (gear icon). Choose “System” from the left menu. Click “Troubleshoot”.
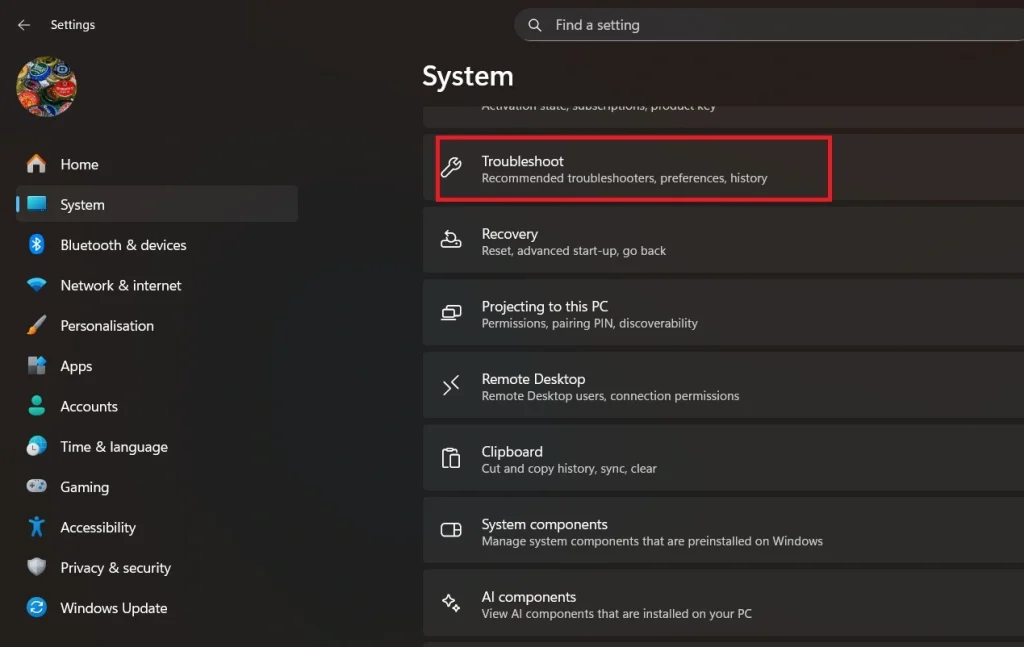
- Select “Other troubleshooters”.
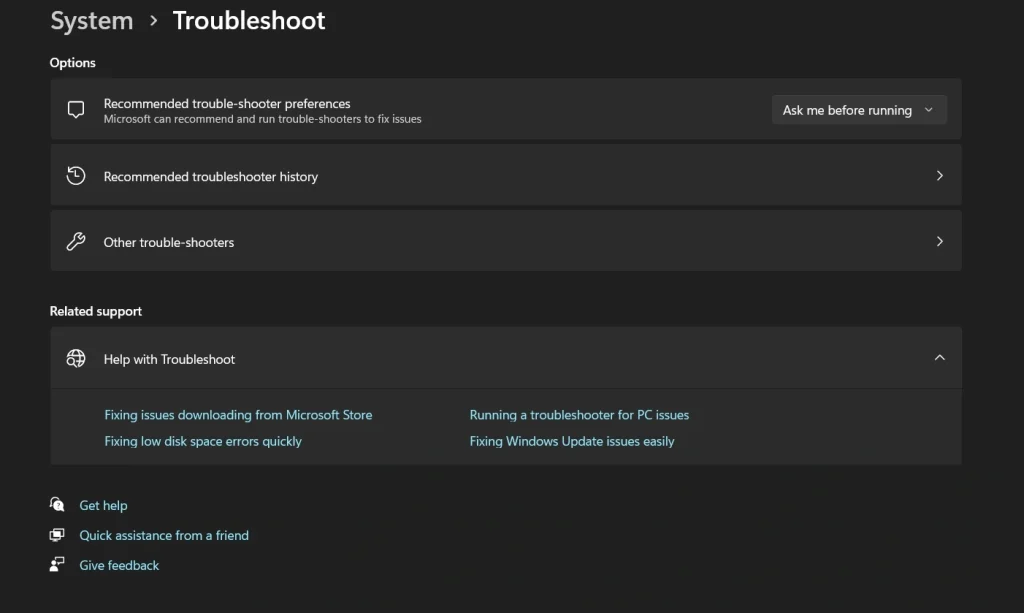
- Find the issue type you need. Click “Run” next to the appropriate troubleshooter.

Method 2: Through Control Panel
Control Panel offers the classic Windows troubleshooting experience. This method works well for advanced users. It provides more detailed options and legacy troubleshooters.
Some older troubleshooters only appear in Control Panel. This method also works if the Settings app has problems. Power users often prefer this traditional approach.
- Press Windows key + R. Type “control” and press Enter. Click “Troubleshooting”.
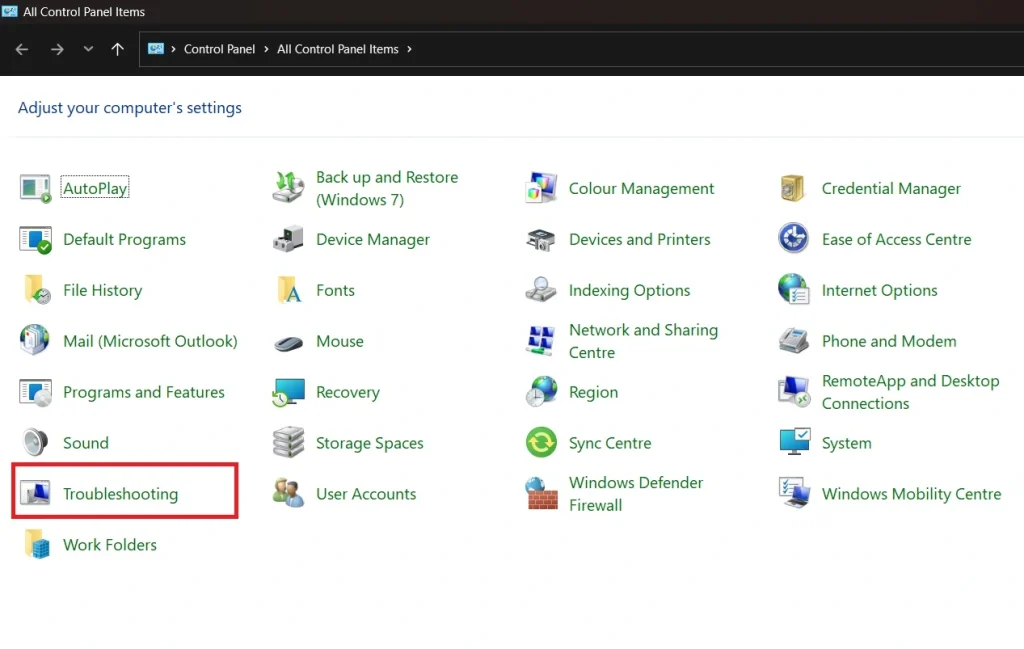
- Choose your problem category. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Method 3: Quick Access
Quick access saves time when you need troubleshooters fast. This method uses the Windows search feature. It’s perfect for users who know exactly what they need.
Search helps you jump directly to specific troubleshooters. You skip multiple menu clicks. This approach works even if you don’t remember the exact location of tools.
- Right-click the Start button. Select “Settings”. Use the search box to type “troubleshoot”.
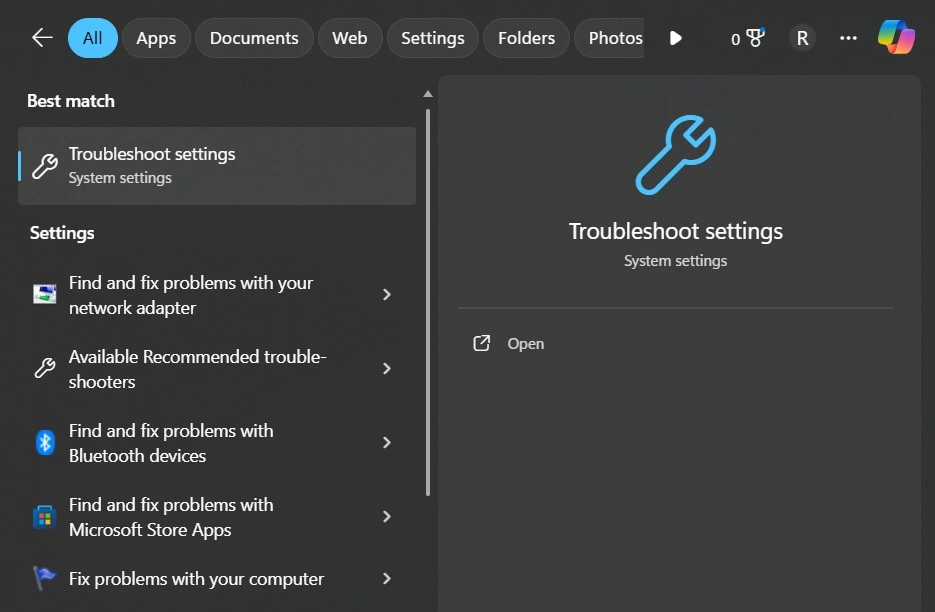
- Click on the relevant result.
For Windows 10:
The Settings app in Windows 10 keeps all troubleshooters organized. This method is user-friendly and modern. It works great for beginners who want simple navigation.
The Settings app shows troubleshooter status clearly. You can see which tools ran recently. The interface explains what each troubleshooter does before you run it.
- Press Windows key + I. Click “Update & Security”. Select “Troubleshoot” from the left panel. Choose “Additional troubleshooters”.
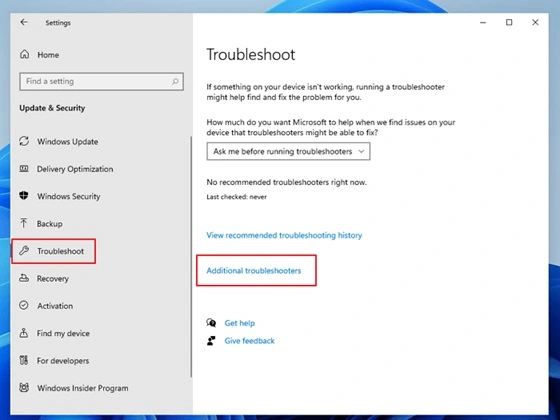
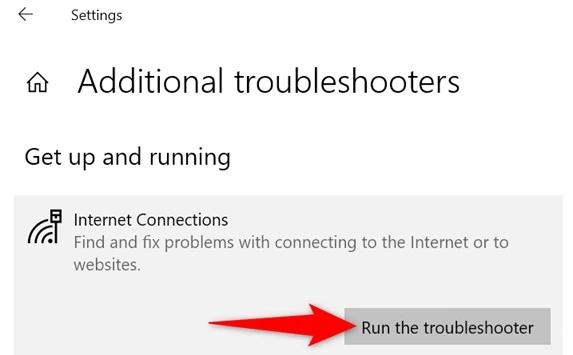
- Pick the troubleshooter you need. Click “Run the troubleshooter.”
Common Troubleshooters Available for Windows 11/10:
- Internet Connections – Fixes network and WiFi problems. Helps restore access when you’re unable to connect or facing slow speeds.
- Audio – Resolves sound and speaker issues. Repairs problems with playback, volume, or missing audio devices.
- Windows Update – Fixes update download problems. Helps when updates fail to install or get stuck.
- Printer – Solves printing and scanner issues. Restores communication between your PC and connected devices.
- Bluetooth – Repairs wireless device connections. Fixes pairing failures and missing Bluetooth options.
- Power – Optimizes battery and sleep settings. Adjusts configurations to improve battery life and prevent sleep-related issues.
- Hardware – Detects device driver problems. Identifies missing, outdated, or malfunctioning drivers.
- Apps – Fixes Microsoft Store and app issues. Helps when apps won’t open, crash, or fail to install.
When you run a troubleshooter for PC issues Windows, it will scan your system. The tool shows a progress bar. It lists what it’s checking. If problems are found, it offers to fix them automatically. Always read the suggested fixes before applying them.
Author’s Tip
Start with the most obvious troubleshooter first. If you have sound problems, try the Audio troubleshooter. For internet issues, use the Network troubleshooter. This saves time and gets better results.
Don’t run multiple troubleshooters at once. Let each one finish completely. Running several tools together can cause conflicts. This might create new problems instead of fixing old ones.
Keep your Windows system updated. New troubleshooters come with updates. They fix more recent problems. Updated troubleshooters work better than old versions. Check for updates monthly to get the latest fixes.
Conclusion
Windows troubleshooters are powerful tools for fixing PC problems. They offer quick, free solutions for common issues. Learning to run a troubleshooter for PC issues Windows makes you more independent with computer problems.
These tools aren’t perfect, but they solve most everyday problems. Try them before calling tech support or paying for repairs. With practice, you’ll fix PC issues faster and easier than ever before.
FAQs:
Q: How long does it take to run a troubleshooter for PC issues on Windows?
Most troubleshooters finish within 2-5 minutes. Complex problems might take longer. The tool shows progress, so you know how much time is left. Simple network fixes happen quickly, while hardware scans take more time.
Q: Can troubleshooters make my PC problems worse?
Windows troubleshooters are very safe. They use tested Microsoft fixes. The tools create restore points before major changes. If something goes wrong, you can undo the changes. Always backup important files first as an extra precaution.
Q: What should I do if the troubleshooter doesn’t fix my problem?
Try a different troubleshooter if available. Check Windows Update for newer fixes. Search online for your specific error message. Contact Microsoft support or a local technician for complex hardware problems that troubleshooters cannot resolve.
Popular Post
Recent Post
How to Upgrade Computer RAM: Complete Guide
Upgrading RAM is one of the simplest ways to improve a computer. It helps the system feel faster and smoother. Apps open quicker. Browsers handle more tabs. Games and tools run with less delay. Many users search for how to upgrade computer RAM because it gives real results without high cost. You do not need […]
How To Clean Your Computer Keyboard: Complete Guide
A computer keyboard is touched more than almost any other device you own. It is used during work, study, gaming, and casual browsing. Fingers carry natural oils, sweat, and dirt. Small food crumbs fall between keys without notice. Dust settles each day slowly. Over time, this creates a hidden layer of grime. Many users do […]
Computer Mouse Buying Guide for Beginners and Advanced Users
Buying a mouse looks easy at first. Many people think all mouse work the same way. Well, that idea often leads to regret later. A mouse affects comfort, speed, and daily work. It matters for office tasks, gaming, design, and study. The right choice reduces strain and improves control. The wrong one feels annoying every […]
How To Overclock a Computer: A Complete Guide
Overclocking is the process of making your computer run faster than its factory settings. It mainly affects the processor, graphics card, and sometimes memory. Many people choose this method to improve performance without buying new hardware. It is popular among gamers, video editors, and users who run heavy software. When done properly, overclocking can give […]
How To Find Password Saved on This Computer: Complete Guide
Many people forget their login details at some point. It happens often. We create many accounts every year. Each one needs a username and a password. Over time, it becomes hard to remember all of them. That is why computers offer ways to store login details. These saved details help users sign in faster. They […]
How To Open/Access Computer Management & Advanced Tips
Every Windows computer has many hidden tools. Most users never see them. They only use basic settings. They change wallpapers. They install apps. They adjust sound and display. That is enough for daily work. But problems still happen. The system slows down. Storage fills up. Errors appear without warning. At this stage, normal settings do […]
How To Transfer Photos From Android Phone To PC/Laptop [2026]
Moving photos from a phone to a computer is something most people need to do often. Phones fill up fast. Photos also matter more than apps. You may want a safe backup. You may want to edit images on a bigger screen. This guide explains how to transfer photos from Android to PC without stress. […]
Top 9 Browsers With Built-In VPN – VPN Browser
Online browsing is no longer private by default. Every website collects data in some form. This includes location details, device information, and browsing habits. Over time, this data builds a clear picture of user behavior. Many people are now uncomfortable with this level of tracking. A VPN browser helps reduce this exposure. It adds a […]
AI In Cyber Security: Who is Winning, Hackers or Security Companies
Cybersecurity once followed clear rules. Companies built firewalls. Users created passwords. Antivirus tools scanned files and removed known threats. When an attack happened, security teams studied it and added new rules. This method worked for many years. It created a sense of control and stability. That sense is gone today. Artificial intelligence has changed how […]
The Biggest AI-Run Cyber Attacks Of All Time
Artificial intelligence is now part of everyday technology. It helps people search faster. It improves medical research. It supports businesses in making better choices. But AI is not used only for good purposes. Cyber criminals have also learned how to use it. This has changed the nature of cyber attacks across the world. In the […]